This dimension is part of the
Positive Climate for Learning priority.
Navigate the FISO Improvement Model
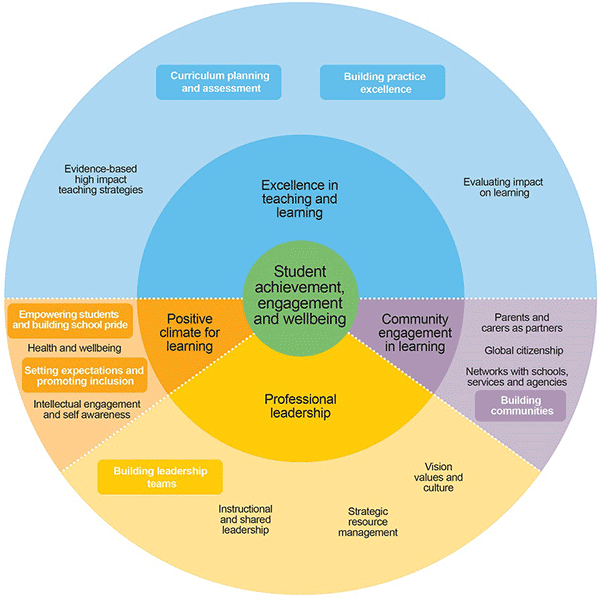
Definition
- Students learn best when they are engaged in work that is interesting, personally relevant, appropriately challenging and when they receive regular feedback on their progress.
- Teaching for intellectual engagement involves the design of authentic tasks that develop students' critical and creative thinking, teamwork, negotiation, decision-making, synthesis and problem solving skills.
- When teachers have high expectations of student learning, students know they are respected as learners and that teachers believe they can succeed.
- To challenge students at their point of learning need, effective teachers collect robust evidence of student learning and use it to target their teaching.
- They use formative assessment to refine their teaching in response to individual learning needs, through identifying the source of student misunderstandings and understanding what each student is ready to learn next.
- Explicitly teaching students metacognition strategies supports them to evaluate their own progress, self-regulate and take responsibility for their own learning.
- Supportive and inclusive schools deliberately foster school connectedness and engagement with learning, especially for those students who are at risk of falling behind or disengaging with school.
Essential Elements
A number of elements are essential to enable effective work within the Framework for Improving Student Outcomes. Eight Essential Elements form the foundation upon which improvement is built.
The Essential Elements for Intellectual engagement and self-awareness are:
Essential Element 4: Student voice, leadership and agency in own learning activated so students have positive school experiences and can act as partners in school improvement.
Essential Element 7: Data collection, analysis and evaluation of student learning growth over time.
The Essential Elements are evident at the Evolving stage of each Continuum (below) and are further articulated in the Embedding and Excelling stages in some dimensions.
Continuum
The Continuum for
Intellectual engagement and self-awareness describes a range of proficiency levels (Emerging, Evolving, Embedding and Excelling) that assists principals and teachers to identify areas of practice that require attention in order to deliver improved student outcomes.
Component: The school has a culture of high expectations
Emerging
Teachers are aware of the importance of maintaining high expectations for all students. Teachers use data to formulate common learning goals for students.
Evolving
The school communicates high expectations about all aspects of schooling, including school attendance, behaviour, learning progress and school completion. Student’s learning growth is regularly measured and informs goal setting for individual students. Teachers and students set individual learning goals together and teachers help students see their progress.
Embedding
Teachers support students to understand and share the high expectations set for them and the steps they need to take to reach these. They consistently and appropriately challenge students. Analysis of student assessment data, using strategies such as item analysis and identifying zone of proximal development, underpins and informs goal setting for individual students. The school supports parents/carers to positively reinforce the high expectations that have been set for their child. Teachers and students collaborate to identify the steps that need to be taken.
Excelling
Students set high expectations for themselves and their peers and support each other to reach these high expectations. A detailed analysis of student outcomes data enables teachers to support and challenge all students to reach their potential. A whole of community commitment to the school’s vision, values and high expectations policies supports a learning environment that maximises success for all students.
Component: Students apply metacognitive strategies to their learning
Emerging
Teachers encourage students to be self-reflective learners by exploring their thinking processes. They emphasise that a person’s ability to learn is not fixed and that effective learning strategies can be learned to improve performance.
Evolving
Teachers introduce students to a number of differentiated learning strategies that may be applied to complete a range of problems. Students are given strategies to set goals and monitor their own progress. Teachers explain how to make informed choices about which strategies to use in particular situations to achieve the learning goals. They support students to adopt a growth mindset.
Embedding
Teachers give students a choice of learning activities based on agreed goals. They encourage students to reflect critically on the strategies they have used to complete the task and to articulate which learning strategies are most effective for them. Teachers support students to actively engage with their learning goals, to plan, monitor and evaluate their own learning. Students trial different strategies to enhance their thinking and learning.
Excelling
Teachers provide students with rich open-ended tasks and students approach the work using a range of individual and collaborative techniques. Teachers effectively diagnose individual students’ abilities, in order to explicitly teach using tailored strategies that are appropriately challenging. All teachers support students to set personal and academic goals and to negotiate tailored learning opportunities to achieve these goals. Students explore and apply a range of thinking strategies appropriate to the task.
Component: The school supports and fosters intellectual engagement
Emerging
Individual teachers are supported to analyse and interpret student assessment data and student feedback and use it to inform their teaching practice. Teachers work independently and generally prepare one lesson for a whole class. Teachers increase student engagement by creating lessons that reflect student interests and stimulate their curiosity.
Evolving
The school invests in time, tools and training to build all teachers’ capability in student assessment and targeted teaching. Teachers work together to develop lesson plans and assessments that cater for different levels of ability and interests. Teachers build on prior knowledge, focus on learning goals and scaffold new learning to engage students and build confidence. Lessons are developed with different student abilities and interests in mind.
Embedding
Teachers work collaboratively to collect evidence of student learning and develop targeted teaching strategies which develop engagement, curiosity and academic rigour. Teachers design challenging activities that involve student choice, deep understanding, discipline-rich inquiry, problem solving and collaboration. Teachers identify individual student needs and monitor learning growth based on student feedback. Teachers modify and adapt instruction to each student’s ability and provide feedback to assist all learners to continually improve their learning.
Excelling
All teachers collect rigorous evidence of learning, target their teaching and evaluate the impact of individual, team and school level practice. Teachers use formal and informal assessment, student input and teaching team collaboration for evaluation and planning which ensures all students are engaged, challenged and extended. Students are intrinsically motivated, independent learners. They monitor their own progress and identify and communicate their learning needs to their teachers. Students feel safe taking risks in their learning. The school works with the community to create a culture of mutual responsibility for independent learning.
Case studies
To see examples of how schools in Victoria are implementing the FISO dimension: Intellectual engagement and self awareness see: Intellectual engagement and self awareness case studies.
Evidence base
To view the evidence base for the FISO positive climate for learning priority area see:  Evidence - Positive climate for learning evidence base
Evidence - Positive climate for learning evidence base
FAQs
Why should my school engage with this dimension?
Research has found that teachers’ expectations of their students can become a self-fulfilling prophecy. Students that teachers expect to do well tend to achieve better, while students who are expected to do poorly tend to fulfil their teachers’ expectations as well. Hattie found an effect size of 0.43 for expectations.
To what extent is this dimension being implemented in my school?
Consider whether teachers have high expectations of student learning and create an environment that challenges each student to reach their potential.
What can my school focus on?
- Metacognitive strategies that help students think about their own learning more explicitly
- Specific strategies for students to set goals and monitor their own progress
- School communication about school completion expectations and post compulsory options
- Engagement strategies designed around individual students, particularly those at risk.
What does successful implementation look like?
- Supportive and inclusive schools deliberately foster school connectedness and engagement with learning, especially for those who are at risk of falling behind or dropping out
- Metacognition approaches are used to help students think about their own learning more explicitly
- Targeted programs help engage at-risk students, addressing their personal wellbeing and develop cognitive, social and emotional skills
- Teachers, parents and peers have high expectations of all students and themselves.
What strategies and actions can my school implement?
- Develop and implement a positive and respectful learning culture
- Implement a specific program to improve retention rates
- Focus on engagement strategies
- Build staff understanding and capability in using metacognitive approaches.
More information
For more information, see:
Positive Climate for Learning priority